Several years ago, a promising therapeutic using stem cell factor (SCF) emerged that could potentially treat a variety of ailments, such as ischemia, heart attack, stroke and radiation exposure. However, during clinical trials, numerous patients suffered severe allergic reactions and development of SCF-based therapeutics stopped.
A research team led by engineers at The University of Texas at Austin has developed a related therapeutic that they say avoids these major allergic reactions while maintaining its therapeutic activity. The keys to the discovery, published recently in Nature Communications, were the use of a similar, membrane-bound version of SCF delivered in engineered lipid nanocarriers.
"We envision this as something you can inject where you have lack of blood flow and it could induce blood vessels to grow in that area," said Aaron Baker, a professor in the Cockrell School of Engineering's Department of Biomedical Engineering, and one of the leaders on the project.
 Stem cell factor is a cytokine, a type of soluble protein that can stimulate regeneration in the body and growth of stem cells. Its ability to help stem cells grow, especially in critical places like bone marrow, makes it very promising for many therapeutic applications. But when delivered to the body in clinical trials related to strokes, it caused mast cell growth, which activated the immune system’s defenses and led to the allergic reactions.
Stem cell factor is a cytokine, a type of soluble protein that can stimulate regeneration in the body and growth of stem cells. Its ability to help stem cells grow, especially in critical places like bone marrow, makes it very promising for many therapeutic applications. But when delivered to the body in clinical trials related to strokes, it caused mast cell growth, which activated the immune system’s defenses and led to the allergic reactions.
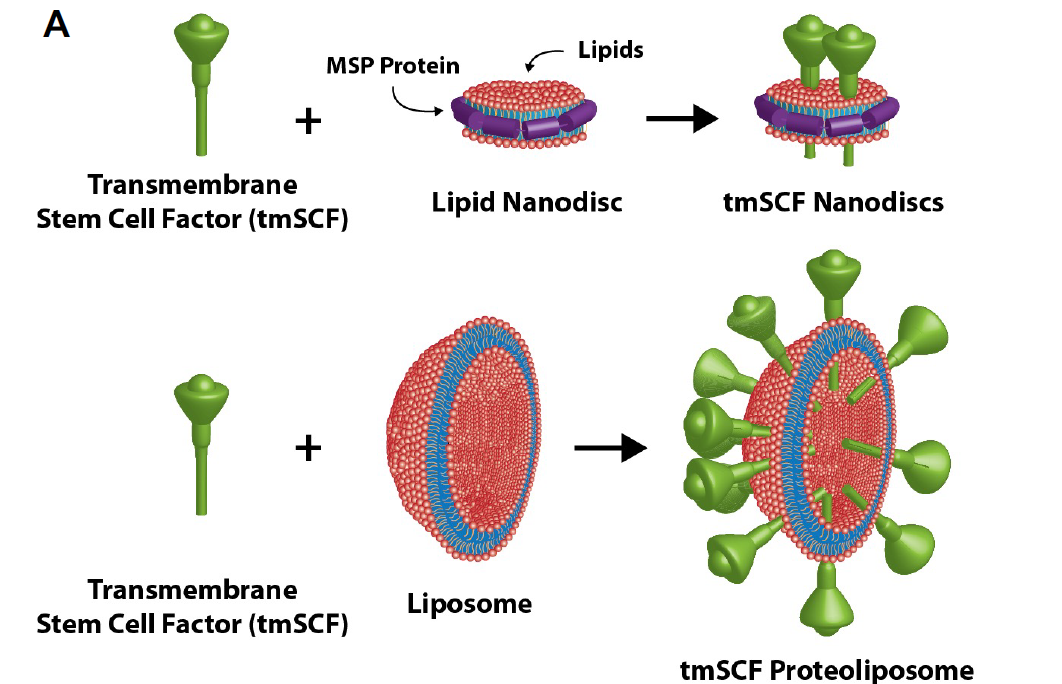
The new therapeutic uses transmembrane stem cell factor, a version of the cytokine that tethered to a cell membrane. In the body, the transmembrane form can be cleaved off into to the soluble form, which travels around the body.
"We found this transmembrane stem cell factor has all the necessary therapeutic properties and without activating the immune system and causing allergic reaction," said Eri Takematsu, a former member of Baker’s lab who is now a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford and was the first author on the paper.
The big problem with the transmembrane SCF is that, because it’s not soluble, it tends to just clump together in solution. So, the team developed lipid nanocarriers to help it say in solution and to tailor its activity towards different cell type. They looked specifically at using a liposomes (lipid bubbles) and lipid nanodiscs as carriers for transmembrane SCF.
"This type of nanodisc is something people haven't explored very much developing therapeutics before," Baker said. "It makes a little island of lipid around the transmembrane SCand holds it together with a ring of proteins, kind of like a lariat."
The researchers have patented their method, and the next step would be clinical trials. In order to do that, however, they need approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to classify the therapeutic as an investigational new drug. In addition, they are continuing to fine-tune important details like correct dosage for patients.
Other team members on the project include Miles Massidda, Jeff Auster, Po-Chih Chen, ByungGee Im, Sanjana Srinath, Sophia Canga, Aditya Singh, Marjan Majid and Andrew Dunn from the Department of Biomedical Engineering; Michael Sherman from the Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston; and Annette Graham and Patricia Martin of the Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences at Glasgow Caledonian University in Scotland. The research was funded through grants from the American Heart Association, National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Department of Defense's Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs.







